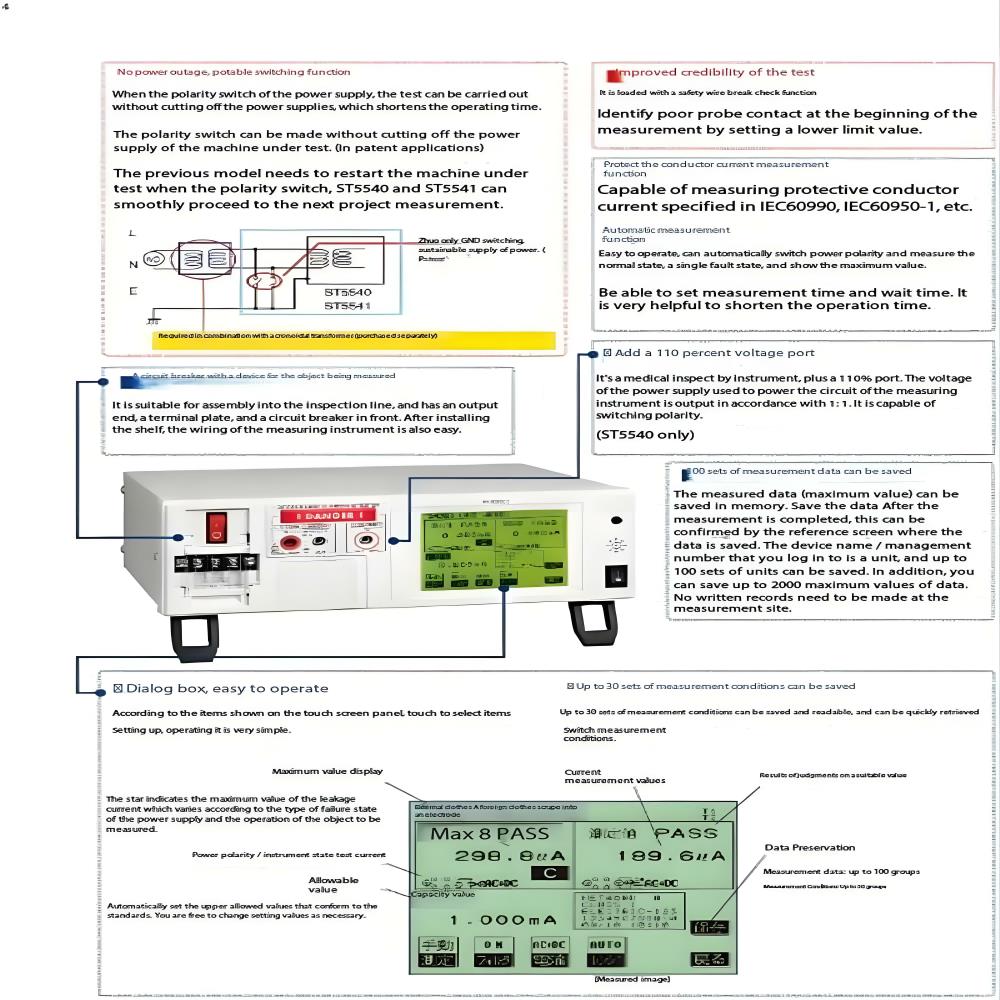
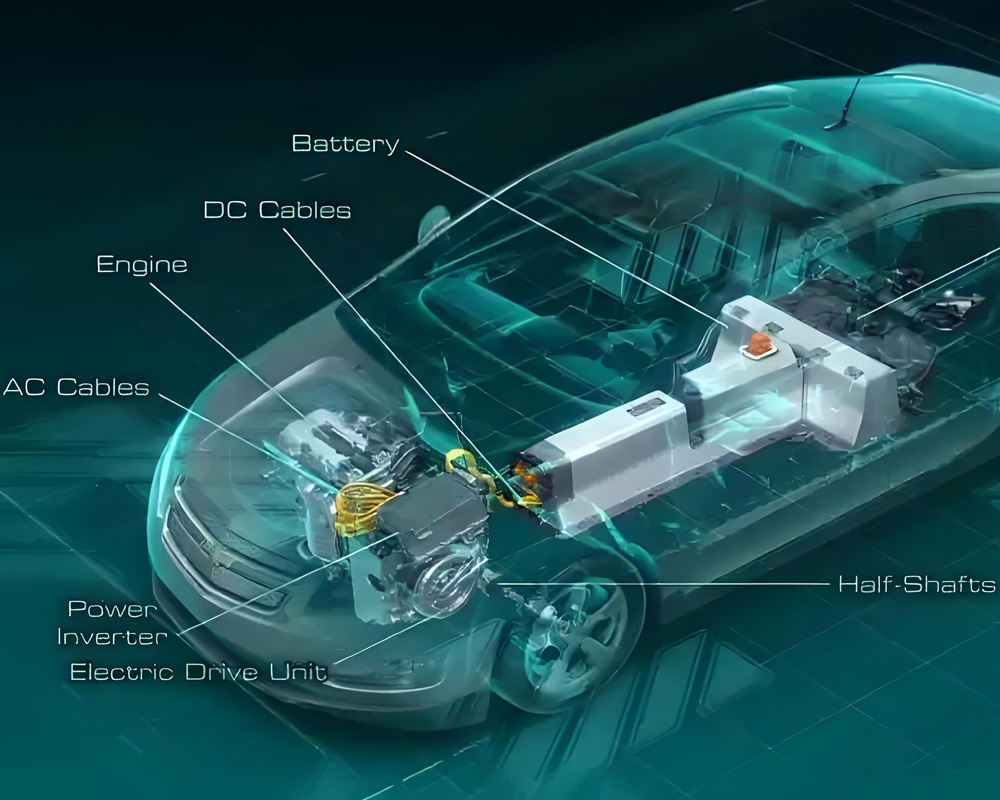
Extreme Testing of New Energy Vehicles: Three Highs Testing, Component Environmental Testing, and Durability Testing
Feb 10, 2025
In the era of the rapid development of new energy vehicles, the discussion of their extreme testing is no longer a topic limited among technicians; instead, it is closely related to the vital interests of every consumer. As the market demand for new energy vehicles continues to grow, the performance of vehicles in extreme environments has become a key criterion for measuring their performance and reliability.
From the stringent tests of the vehicle's three highs testing, to the meticulous inspection of components, and then to the long - term challenge of the vehicle's durability testing, each link is a deep exploration of the technological limits of new energy vehicles. These tests not only showcase the forefront of technology but also provide a comprehensive guarantee for the vehicle's safety and durability. Therefore, understanding the details of these extreme tests is an important window for each of us to perceive the future development trends of automobiles.
Vehicle Three Highs Testing: The Ultimate Inspection in Extreme Environments
Vehicle three highs testing is one of the standard tests for new energy vehicles, and its importance cannot be overstated. This series of tests includes three major links: high - temperature, high - altitude, and high - cold, aiming to test the performance and reliability of the entire vehicle under the harshest natural conditions.
First is the high - temperature test, usually carried out in Turpan, Xinjiang, where the surface temperature in summer can reach up to 70°C. Under such extreme high - temperature conditions, the vehicle's thermal management system and the safety performance of the battery will face severe challenges. It tests whether the vehicle can maintain normal operation in an overheated environment and whether it has effective heat dissipation strategies and overheat protection mechanisms.
Test Conditions:
High - temperature exposure > 6h
Temperature higher than 35°C
Total driving mileage should be no less than 10,000 km, with no less than 2,000 km on urban roads, no less than 3,000 km on rural roads, and no less than 5,000 km on highways.
Subjective Evaluation Tests:
Evaluation of power performance, drivability, NVH performance, electrical performance, etc.
Evaluation of air - conditioning cooling and comfort
Inspection of daily function operations
Objective Evaluation Tests:
Collection of key - point temperatures during the test under different working conditions
Monitoring of temperature changes and working status
Engine - related Tests:
Engine Shutdown Protection (Test condition: Temperature 40°C - 60°C): To prevent the engine from being damaged due to overheating, which may affect its service life.
Engine Matching Test (Test condition: Temperature 40°C - 60°C): To ensure the matching of the engine and its accessory systems (such as the cooling system, fuel system, and emission system) under high - temperature conditions.
Other Tests:
Light Aging Test (Test condition: Temperature 40°C - 60°C): To evaluate the performance and durability of automotive components, materials, and the entire vehicle under long - term exposure to sunlight.
High - temperature Range Test (Test condition: Temperature higher than 35°C): The vehicle drives from SOC100 to 0%, and the vehicle's range and energy consumption rate are statistically analyzed.
High - temperature Charging Test (Test condition: Temperature higher than 35°C): The power battery is discharged to SOC 0% and then charged to full. The charging efficiency = (electricity entering the power battery / electricity from the charging network) * 100%. Also includes forward function testing, reverse function testing, software function testing, scenario simulation testing, extreme function testing, user function experience testing, etc. And temperature testing of the ECU (Electronic Control Unit) and various sensors, electrical system performance testing, basic calibration (such as chassis system calibration), etc.
The high - cold test is completely the opposite. It is often carried out in places like Heihe and Hailar, where the ambient temperature is as low as - 30°C. In such a low - temperature environment, the chemical reaction rate of the battery will drop significantly, affecting the vehicle's range and power output. The focus of the test is the response speed and efficiency of the battery heating system, as well as the battery's discharge performance and low - temperature protection mechanism in severe cold conditions.
Test Road Types:
High - speed snow loop, snow dynamic square, ice dynamic square, ABS open - circuit, ice and snow roundabout, handling stability road, checkerboard road, snow - melting pool, split - slope ramp
Test Conditions:
Vehicle soaking > 12h
Temperature lower than - 10°C
Total driving mileage should be no less than 10,000 km, with no less than 2,000 km on urban roads, no less than 3,000 km on rural roads, and no less than 5,000 km on highways.
Subjective Evaluation Tests:
Evaluation of power performance, drivability, NVH performance, electrical performance, controllability, braking performance, suspension system performance, etc.
Objective Evaluation Tests:
Starting Performance Test (Test condition: Ambient temperature - 20°C to - 40°C): To evaluate the cold - start performance, power, efficiency, and reliability of the engine.
Heating Performance Test (Test condition: Ambient temperature - 20°C to - 40°C): Collection of key - point temperatures during the test under different working conditions, and monitoring of the temperature changes and working status of the ECU (Electronic Control Unit) and various sensors.
Defrosting Performance Test (Test condition: Ambient temperature - 20°C to - 40°C): With the blower at the maximum setting and full - warm defrosting, pay attention to the field of view of the front windshield area and the exterior rear - view mirror during the test.
Other Tests:
Snow - covered Area Passability Test (Test condition: Ambient temperature - 10°C to - 40°C): Tests include snow - covered road passability test and snow - covered slope passability test.
Snow - blowing Test (Test condition: Ambient temperature - 20°C to - 40°C, with a snow - blower set on the high - speed snow loop): To detect whether there is snow accumulation and icing in the front cabin, fan, trunk, lamps, etc., and the operation of functions.
Low - temperature Range Test (Test condition: Ambient temperature - 20°C to - 40°C): The vehicle drives from SOC100 to 0%, and the vehicle's range and energy consumption rate are statistically analyzed.
Low - temperature Charging Test (Test condition: Ambient temperature - 20°C to - 40°C): The power battery is discharged to SOC 0% and then charged to full. The charging efficiency = (electricity entering the power battery / electricity from the charging network) * 100%. Also includes forward function testing, reverse function testing, scenario simulation testing, software function testing, extreme function testing, user function experience testing, etc. And calibration of various system and performance parameters of the vehicle in a cold environment, such as engine performance calibration, air - conditioning system performance calibration, basic calibration, "three - electric" system calibration, thermal management system calibration, chassis system calibration.
Finally, the high - altitude test is mainly carried out in areas above 4,000 meters above sea level to detect the electrical safety of new energy vehicles in a low - oxygen environment and the stability of the motor and electronic control systems. In the high - altitude environment, the air is thin, and the insulation performance between electrical equipment will be tested, and arcs are likely to occur. Therefore, this test focuses on whether the vehicle's electrical system can maintain stable operation under oxygen - deficient conditions and the effectiveness of its safety protection measures.
Typical regions for three - high tests
Through vehicle three highs testing, not only can the adaptability of new energy vehicles in extreme environments be comprehensively evaluated, but also direct and effective data support can be provided for subsequent technological improvements, ensuring that new vehicle models have sufficient environmental adaptability and safety guarantees when they are launched on the market.